Download the presentation of this section.
The Dual coding theory was developed by Allan Paivio in 1971. Its idea is using different types of stimuli to help learners encode information in their brains more effectively, enabling it to be more easily retrieved later on. In the classroom, the main two types of stimuli that are used are visual and verbal.
On ‘Future learn‘ Oliver Caglioli explians how Dual Coding Theory can support the building of knowledge and understanding.
The working memory consists of two cognitive workspaces: one encodes and processes images and events (non-verbal information) while the other does so with language (verbal information). By engaging both working memory, you process twice as much. Then, verbal and non-verbal (visual) information is stored separately in long-term memory.
Visuals (images, graphs, diagrams, photos, animations, videos, illustrations …) are more powerful: written or spoken text is stored once, but pictures of words are stored twice; verbally and visually. By presenting information in two ways (verbal and visual), it enters the brain in both ways, so it is stored twice and therefore better in long-term memory.
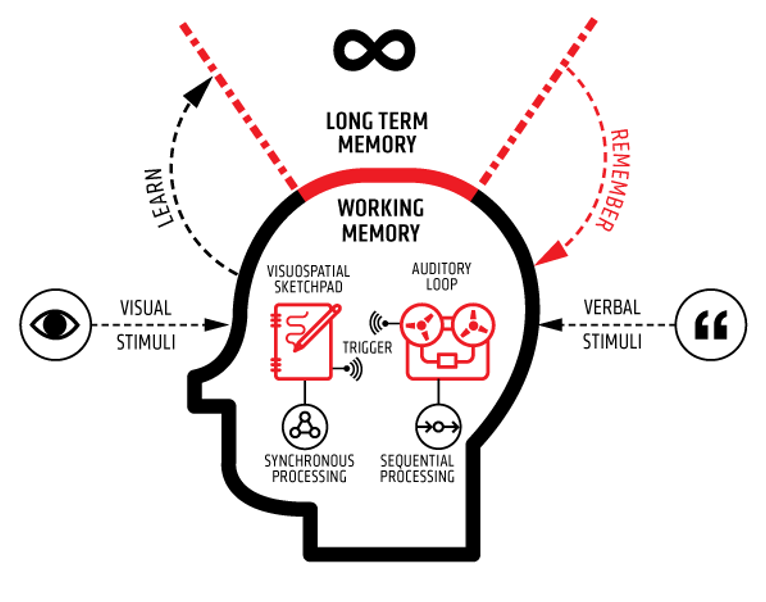
Suppose you want to explain the difference between a raster map or a vector map. You can of course do this by text only, but it is much better to combine it with a specific image attached to it.